2021. 10. 27. 16:44ㆍAI/Deep Learning
Batch Normalization
Definition
- 인공신경망을 re-centering과 re-scaling으로 layer의 input 정규화를 통해 더 빠르고 안정화시키는 방법
Motivation
Internal covariate shift
- Covariate shift : 이전 레이어의 파라미터 변화로 현재 레이어 입력 분포가 바뀌는 현상
- Internal covariate shift : 레이어 통과시 마다 covariate shift가 발생해 입력 분포가 약간씩 변하는 현상
- 망이 깊어짐에 따라 작은 변화가 뒷단에 큰 영향을 미침
- Covariate Shift 줄이는 방법
- layer's input 을 whitening 시킴(입력 평균:0, 분산:1)
- whitening이 backpropagation과 무관하게 진행되기 때문에 특정 파라미터가 계속 커질 수 있음(loss가 변하지 않으면 최적화 과정동안 특정 변수 계속 커지는 현상 발생 가능)
- BN(Batch Normalization)을 통해 조절(평균, 분산도 학습시에 같이 조절됨)


Gradient Vanishing / Exploding problem
- 간접적 방법
- change activation function : Sigmoid 대신 ReLU 사용
- careful initialization : 가중치 초기화를 잘 함
- small learning rate : gradient exploding 방지를 위해 작은 learning rate
- 배치 정규화
- 학습 과정 전체를 안정화 해서 학습속도 가속
Normalization
- local optimum(minima or maxima) 방지

Training
- Input: Values of x over a mini-batch: $\mathcal{B} = {x_{1\ldots m}};$ Parameters to be learned: $\gamma, \beta$
- Output: ${y_i=BN_{\gamma,\beta}(x_i)}$
- $\mu_{\mathcal{B}}\gets \frac 1 m \sum_{i=1}^mx_i$ // mini-batch mean
- $\sigma_{\mathcal{B}}^2\gets \frac 1 m \sum_{i=1}^m(x_i-\mu_{\mathcal{B}})^2$ // mini-batch variance
- $\hat{x_i} \gets \frac {x_i-\mu_{\mathcal{B}}}{\sqrt{\sigma_{\mathcal{B}}^2+\epsilon}}$ // normalize
- $y_i \gets \gamma \hat{x_i}+\beta \equiv BN_{\gamma, \beta}(x_i)$ // scale and shift
- whitening과의 차이점 : 평균, 분산 구한 후 정규화 시키고 scale과 shift연산을 위해 $\gamma, \beta$가 추가되고 정규화 시킨 부분을 원래대로 돌리는 identity mapping도 가능하고 학습을 통해 $\gamma, \beta$를 정할 수 있어 단순하게 정규화만 할 때 보다 강력해짐
- 보통 non-linear activation function 앞에 배치
- BN은 신경망에 포함돼 역전파를 통해 학습 가능하고, 이 때 chain rule 적용
Training vs Test
Training
- mini-batch 마다 $\gamma, \beta$를 구하고 그 값을 저장
Test
- 학습 시 mini-batch마다 구했던 $\gamma, \beta$의 평균을 사용
- 분산 : 분산의 평균에 $\frac m {m-1}$을 곱함(통계학적으로 unbiased variance에는 Bessel's correction을 통해 보정)
- 학습 전체 데이터에 대한 분산이 아니라 mini-batch 들의 분산을 통해 전체 분산 추정 시 통계학적 보정을 위해 베셀 보정값을 곱해주는 방식으로 추정

pseudo code
Input : Network N with trainable parameters $\Theta$; subset of activations ${x^{(k)}}_{k=1}^K$
Output : Batch-normalized network for inference, $N_{BN}^{inf}$
1: $N_{BN}^{tr}\gets N$ // Training BN network
2:
$for\ k = 1\ldots K\ do$3: Add transformation $y^{(k)}=BN_{\gamma^{(k)},\beta^{(k)}}(x^{(k)})$ to $N_{BN}^{tr}$(Alg. 1)
4: Modify each layer in $N_{BN}^{tr}$ with input $x^{(k)}$ to take $y^{(k)}$ instead
5: end for
6: Train $N_{BN}^{tr}$to optimize the parameters $\Theta \cup {\gamma^{(k)},\beta^{(k)}}_{k=1}^K$
7: $N_{BN}^{inf} \gets N_{BN}^{tr}$ // Inference BN network with frozen parameters
8:
$for\ k = 1\ldots K\ do$
9: // For clarity, $x\equiv x^{(k)}, \gamma \equiv \gamma^{(k)}, \mu_{\mathcal{B}}\equiv \mu_{\mathcal{B}}^{(k)},\ etc.$
10: Process multiple training mini-batches ${\mathcal{B}}$, each of size m, and average over them:
$$E[x] \gets E_{\mathcal{B}}[\mu_{\mathcal{B}}]$$
$$Var[x] \gets \frac m {m-1} E_{\mathcal{B}}[\sigma_{\mathcal{B}}^2]$$
- 11: In $N_{BN}^{inf}$, replace the transform $y=BN_{\gamma, \beta}(x)$ with $y= \frac {\gamma}{\sqrt{Var[x]+\epsilon}}\cdot x + (\beta-\frac {\gamma E[x]}{\sqrt{Var[x]+\epsilon}})$
- 12: end forOptimization landscape smoother
- 최적화 문제를 reparametrize함 ⇒ 학습을 빠르고 쉽게함
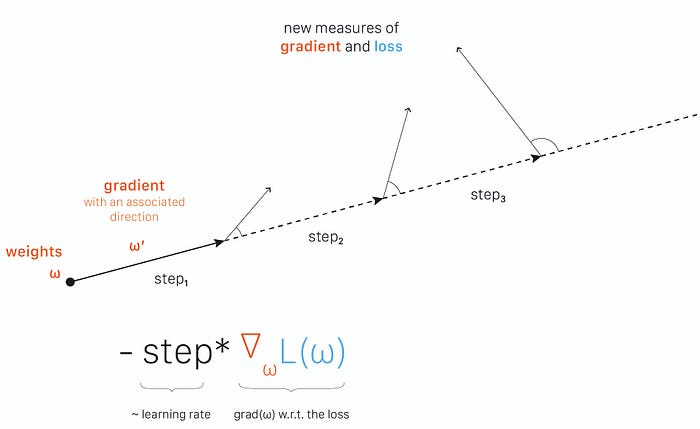
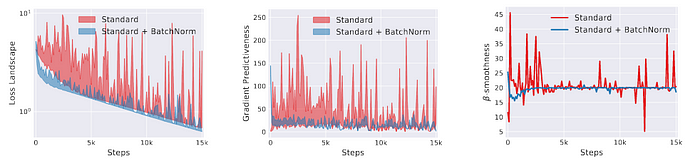
Side Effect
- orthogonality matter 때문에 오버피팅을 피하기 위해 BN에 의존하면 안 됨(한 가지 문제를 다루는데 여러가지 module이 필요하면 더 어려움)
- 배치 사이즈가 커질 수록 regularization이 적게된다.(noise impact를 줄임)
Conclusion
- 단순하게 평균, 분산을 구하는 것이 아닌, $scale(\gamma), shift(\beta)$를 통한 변환으로 유용하게 되고, 신경망의 중간에 BN이 위치하게 되어 학습으로 $\gamma, \beta$를 구할 수 있게 됨
- Covariate shift 문제를 줄여줌 ⇒ 성능 향상, 빠른 학습
Reference
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Batch_normalization
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1502.03167.pdf
https://eehoeskrap.tistory.com/430
https://m.blog.naver.com/laonple/220808903260
https://towardsdatascience.com/batch-normalization-in-3-levels-of-understanding-14c2da90a338
https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2021/03/introduction-to-batch-normalization/
'AI > Deep Learning' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Federated Learning (0) | 2021.12.08 |
|---|---|
| Adam Optimizer (0) | 2021.10.26 |
| Word2Vec (0) | 2021.10.25 |
| CNN(Convolutional Neural Network) (0) | 2021.10.22 |
| Dropout (0) | 2021.10.21 |